Renal System
Published .
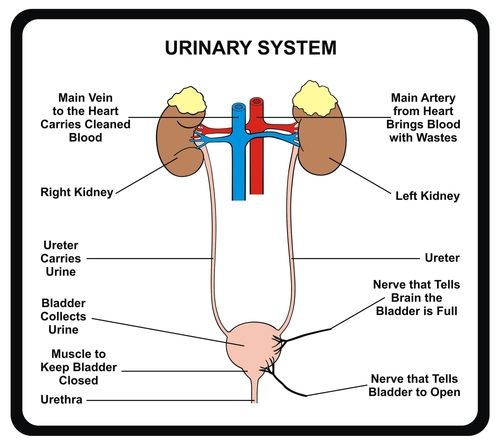
The principal function of the urinary system is to maintain the volume and composition of body fluids within normal limits. One aspect of this function is to rid the body of waste products that accumulate as a result of cellular metabolism, and, because of this, it is sometimes referred to as the excretory system.
Although the urinary system has a major role in excretion, other organs contribute to the excretory function. The lungs in the respiratory system excrete some waste products, such as carbon dioxide and water. The skin is another excretory organ that rids the body of wastes through the sweat glands. The liver and intestines excrete bile pigments that result from the destruction of hemoglobin. The major task of excretion still belongs to the urinary system. If it fails the other organs cannot take over and compensate adequately.
The urinary system maintains an appropriate fluid volume by regulating the amount of water that is excreted in the urine. Other aspects of its function include regulating the concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids and maintaining normal pH of the blood.
In addition to maintaining fluid homeostasis in the body, the urinary system controls red blood cell production by secreting the hormone erythropoietin. The urinary system also plays a role in maintaining normal blood pressure by secreting the enzyme renin.
Components of the Urinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys form the urine and account for the other functions attributed to the urinary system. The ureters carry the urine away from kidneys to the urinary bladder, which is a temporary reservoir for the urine. The urethra is a tubular structure that carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the outside.
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary Bladder
- Urethra
The kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. The kidneys are the organs that filter the blood, remove the wastes, and excrete the wastes in the urine. They are the organs that perform the functions of the urinary system. The other components are accessory structures to eliminate the urine from the body.
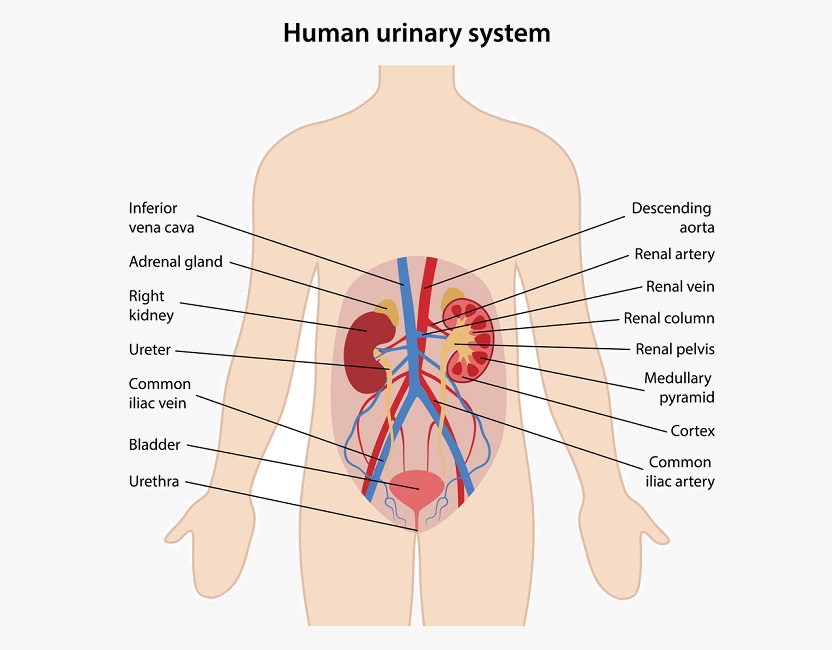
The paired kidneys are located between the twelfth thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae, one on each side of the vertebral column. The right kidney usually is slightly lower than the left because the liver displaces it downward. The kidneys, protected by the lower ribs, lie in shallow depressions against the posterior abdominal wall and behind the parietal peritoneum. This means they are retroperitoneal. Each kidney is held in place by connective tissue, called renal fascia, and is surrounded by a thick layer of adipose tissue, called perirenal fat, which helps to protect it. A tough, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule closely envelopes each kidney and provides support for the soft tissue that is inside.
In the adult, each kidney is approximately 3 cm thick, 6 cm wide, and 12 cm long. It is roughly bean-shaped with an indentation, called the hilum, on the medial side. The hilum leads to a large cavity, called the renal sinus, within the kidney. The ureter and renal vein leave the kidney, and the renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum.
Each kidney contains over a million functional units, called nephrons. A nephron has two parts: a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a cluster of capillaries, called the glomerulus, surrounded by a double-layered epithelial cup, called the glomerular capsule. The juxtaglomerular apparatus, which monitors blood pressure and secretes renin, is formed from modified cells in the afferent arteriole and the ascending limb of the nephron loop.
Each ureter is a small tube, about 25 cm long, that carries urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder. It descends from the renal pelvis, along the posterior abdominal wall, which is behind the parietal peritoneum, and enters the urinary bladder on the posterior inferior surface.
The urinary bladder is a temporary storage reservoir for urine. It is located in the pelvic cavity, posterior to the symphysis pubis, and below the parietal peritoneum. The size and shape of the urinary bladder varies with the amount of urine it contains and with the pressure it receives from surrounding organs.
