The Pancreas
Published (updated: ).
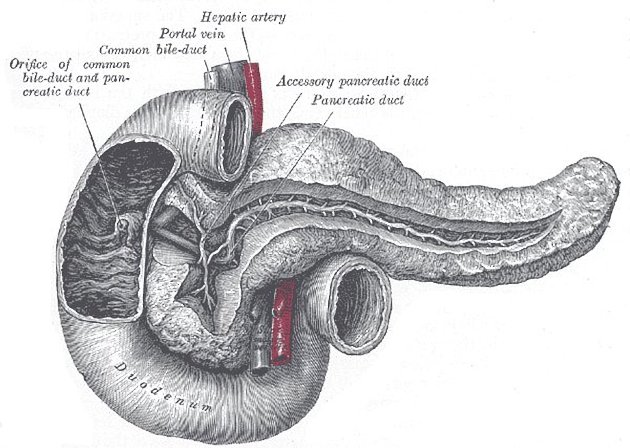
The pancreas is both an exocrine gland as it secretes pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes, and an endocrine gland as it produces several important hormones. It is located just below and behind the stomach. The endocrine cells of the pancreas are grouped together in areas called islets of Langerhans. The islets produce the amino acid-based hormones insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. Insulin and glucagon are both involved in controlling blood glucose levels. Insulin is produced by beta cells and causes excess blood glucose to be taken up by liver and muscle cells, where it is stored as glycogen. Glucagon is produced by alpha cells and stimulates liver cells to break down stores of glycogen into glucose which is then released into the blood. An alpha cell is another type of endocrine cell that is found within the islets of Langerhans.
Hormones Produced In The Pancreas
| Hormone | Effects |
|---|---|
| Insulin | Reduces blood glucose concentration |
| Glucagon | Increases blood glucose concentration |
| Amylin | Body Cells, Bone cells |
| Somatostatin (inhibitory hormone) | Body Cells, Bone cells |
| Ghrelin | Body Cells, Bone cells |
