Blood
Published (updated: ).
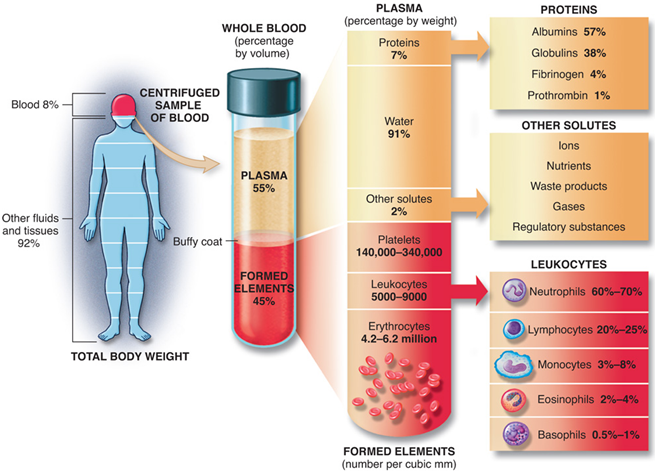
Blood is the fluid of life, transporting oxygen from the lungs to body tissue and carbon dioxide from body tissue to the lungs. Blood is the fluid of growth, transporting nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughout the body. Blood is the fluid of health, transporting disease-fighting substances to the tissue and waste to the kidneys. Because it contains living cells, blood is alive. Red blood cells and white blood cells are responsible for nourishing and cleansing the body. Without blood, the human body would stop working.
Red Blood Cells
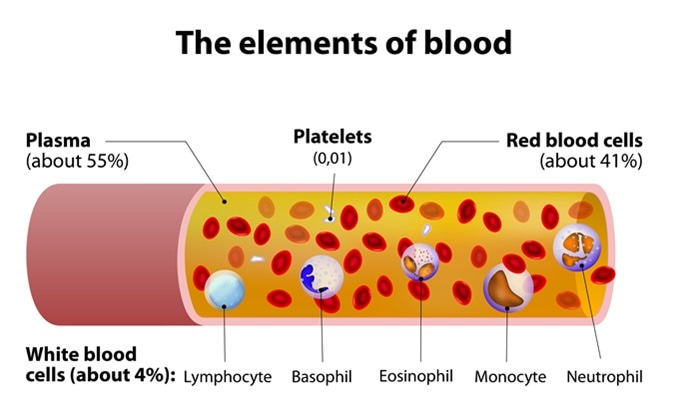
Red blood cells represent 40%-45% of blood volume. They are generated from bone marrow at a rate of four to five billion per hour. They have a lifecycle of about 120 days in the body.
Platelets
Platelets are an amazing part of blood. Platelets are the smallest of the blood cells and literally look like small plates in their non-active form. Platelets control bleeding. Wherever a wound occurs, the blood vessel will send out a signal. Platelets receive that signal and travel to the area and transform into their “active” formation, growing long tentacles to make contact with the vessel and form clusters to plug the wound until it heals.
Plasma
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood. Plasma is yellowish in color and is made up mostly of water, but it also contains proteins, sugars, hormones and salts. It transports water and nutrients to the body’s tissues.
White Blood Cells
Although white blood cells (leukocytes) only account for 1% of blood, they are very important. White blood cells are essential for good health and protection against illness and disease. Like red blood cells, they are constantly being generated from bone marrow. They flow through the bloodstream and attack foreign bodies, like viruses and bacteria. They can even leave the bloodstream to extend the fight into tissue.
Function of Blood
Blood is a type of connective tissue. Connective tissue are tissues (groups of like cells that combine to eventually make an organ) in the body that support, connect, or separates all other types of tissues in the body. Blood is an example of a non-Newtonian fluid that provides protection through shock absorption. Blood is the transportation network for oxygen, CO2, glucose, and other nutrients that that body cells need to exist. White blood cells provide a defense against infectious invaders. Platelets are always standing by to create a blood clot in the event a leak is found in the vast network of blood vessels of the body.
