The Brain Is Still In Charge
Published .
The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system controls specific body processes, such as blood circulation, digestion, breathing, urination, heartbeat, etc. The autonomic nervous system is named so because it works autonomously, i.e., without a person’s conscious effort.
The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is homeostasis. Apart from maintaining the body’s internal environment, it is also involved in controlling and maintaining the following life processes:
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Urination
- Defecation
- Blood pressure
- Sexual response
- Body temperature
- Heartbeat
- Breathing rate
- Fluid balance
There are two types of the autonomic nervous system:
- Sympathetic autonomic nervous system
- Parasympathetic autonomic nervous system
What Is the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System?
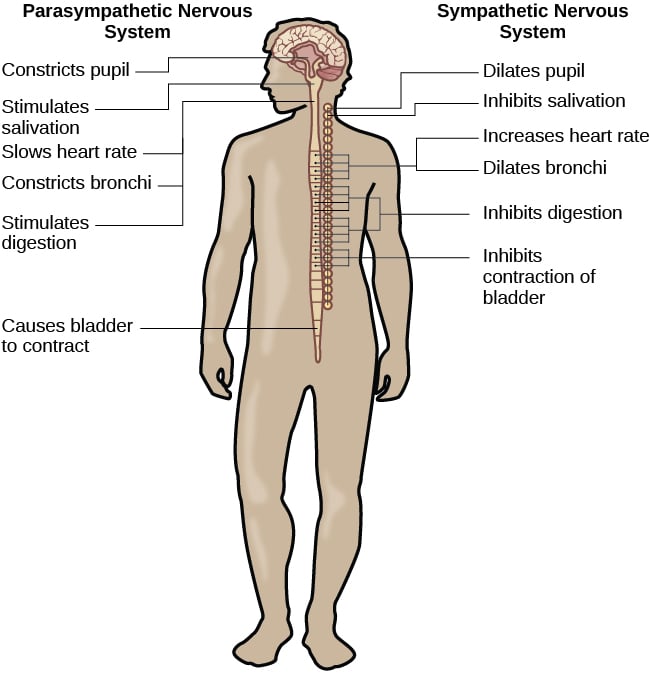
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is the part of the autonomic nervous system located near the thoracic and lumbar regions in the spinal cord. Its primary function is to stimulate the body’s fight-or-flight response. It does this by regulating the heart rate, rate of respiration, pupillary response and more.
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is located in between the spinal cord and the medulla. It primarily stimulates the body’s “rest and digest” and “feed and breed” responses.
Difference between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for the “fight or flight” response during any potential danger. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system inhibits the body from overworking and restores the body to a calm and composed state. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are differentiated based on how the body responds to environmental stimuli.
The major differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are summarised below
| Sympathetic | Parasympathetic |
| Involved in the fight or flight response. | Involved in maintaining homeostasis and also, permits the rest and digest response. |
| The sympathetic system prepares the body for any potential danger. | The parasympathetic system aims to bring the body to a state of calm. |
| Sympathetic system has shorter neuron pathways, hence a faster response time. | Has comparatively longer neuron pathways, hence a slower response time. |
| Increases heartbeat, muscles tense up. | Reduces heartbeat, muscles relaxes. |
| The pupil dilates to let in more light. | The pupil contracts. |
| Saliva secretion is inhibited. | Saliva secretion increases, and digestion increases. |
| In “fight and flight” situations, Adrenaline is released by the adrenal glands; more glycogen is converted to glucose. | No such functions exist in “fight or flight” situations. |
Conclusion
The autonomic nervous system comprises two parts- the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system activates the fight or flight response during a threat or perceived danger, and the parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a state of calm.
