Types of Brain Injuries
Published (updated: ).
Pathophysiology of head and brain injuries
Brain injuries can be the result of increased intracranial pressure or direct or indirect injury. Indirect injury can occur from edema, bleeding, and lack of circulation due to hypotension. Bleeding and edema can increase the pressure inside the cranial vault. There is only so much space in the intact skull, so any bleeding or swelling immediately increases the pressure inside of the skull resulting in pressure applied to the brain.
Brain injuries that result from bleeding
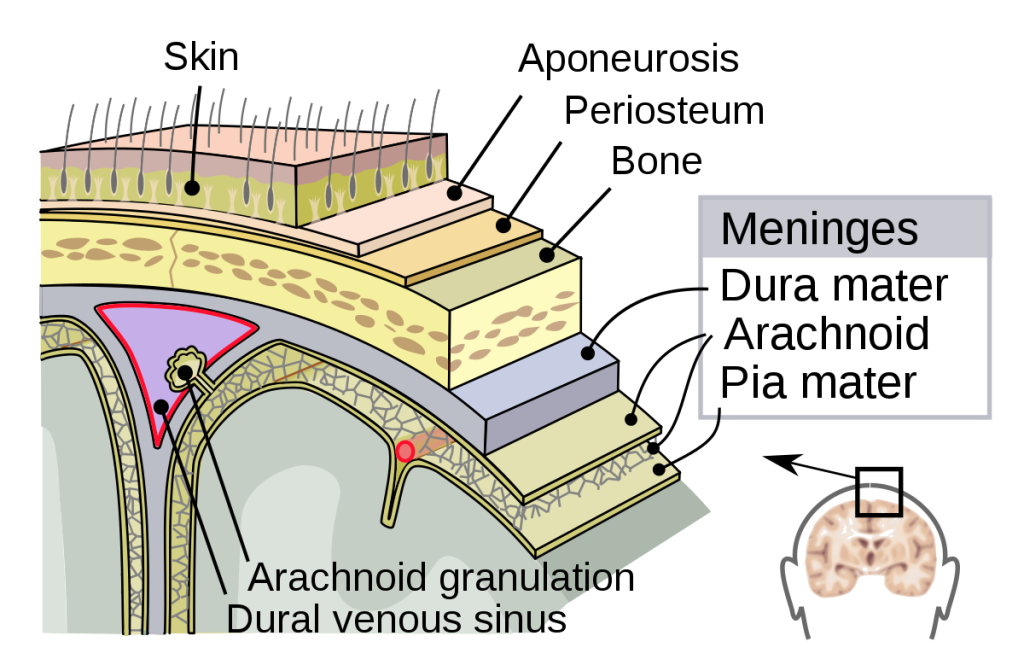
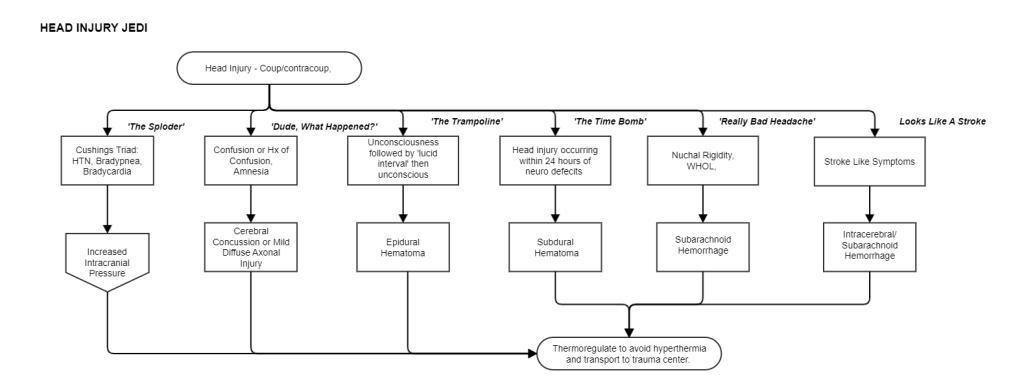
The epidural hematoma is the result of arterial bleeding on top of the dura mater. The sudden spike in intracranial pressure results in immediate loss of consciousness of the patient. Medics should suspect an epidural hematoma anytime they encounter a head injury patient that is either in and out of consciousness or has a history of losing consciousness after the head injury. The epidural hematoma and its nature resulting in a loss of consciousness followed by a lucid interval provides temptation for medics to just assume that the patient is fine. Don’t be fooled by the epidural hematoma.
The subdural hematoma follows a different path than the epidural hematoma. The subdural hematoma is the result of venous bleeding that occurs beneath the dura mater. The bleeding takes time to accumulate in the skull. The patient with a subdural hematoma will sustain a head injury and have no discernible symptoms immediately after the injury. The problem comes 24 hours later when the patient is found with neurological problems associated with a head injury sustained the previous day. The subdural hematoma also provide the temptation for medics to assume that the patient is not injured. Do not be fooled by the subdural hematoma.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage results from bleeding between the cerebral hemispheres. This interesting injury results not only in a headache but also stroke-like symptoms. Medics should suspect an intracerebral hemorrhage when they encounter a patient with a head injury that presents with stroke-like symptoms.
A head injury that results in immediate headache and photophobia should make the medic suspect a subarachnoid bleed. The arachnoids are blood vessels that surround the brain and provide a blood supply. The blood collects in an area between the brain and the dura mater which results in the patient complaining of a terrible headache. Further, the patient may also experience nuchal rigidity. Nuchal rigidity is a stiff neck and is observed when the patient cannot turn their head to the left or to the right.
Direct Injury To The Brain
A concussion is a head injury that results from direct injury to the brain itself. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury. Concussions are only recently being understood for what they really are, which is a serious brain injury. Concussions require medical investigation with imaging and other diagnostic tests. While a concussion may not result in serious disability, the result of a concussion is generally considered to be permanent. Furthermore, concussions on top of concussions can result in poor outcomes for the patient. The primary symptom that the medic should recognize when a patient has a concussion is confusion. Generally there is no report of a loss of consciousness. the following symptoms are also associated with concussions:
- Delayed motor or verbal responses
- Inability to focus attention
- Lack of coordination
- Disorientation
- Inappropriate emotional responses
- Memory deficit – patients with concussions often experience amnesia. retrograde amnesia is a type of Amnesia where the patient cannot recall the events preceding the injury. The memory never returns.
- Inability to recall simple Concepts and words
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
