Sprains & Strains
Published .
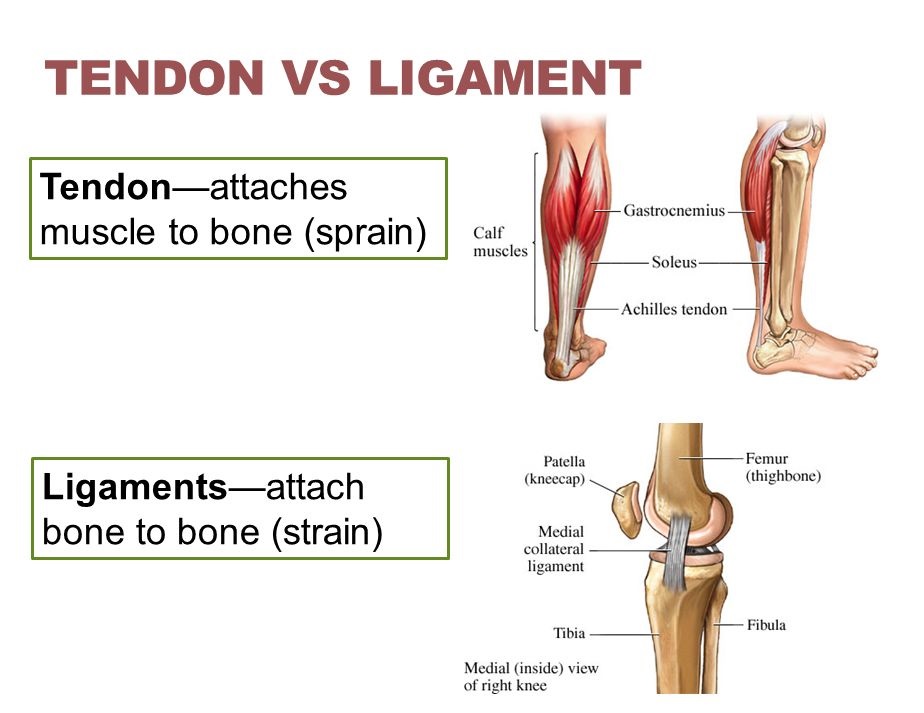
A tendon is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Tendons may also attach muscles to structures such as the eyeball. A tendon serves to move the bone or structure. A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
A sprain is a stretched or torn ligament. Ligaments are tissues that connect bones at a joint. Falling, twisting, or getting hit can all cause a sprain. Ankle and wrist sprains are common. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and being unable to move your joint. You might feel a pop or tear when the injury happens.
A strain is a stretched or torn muscle or tendon. Tendons are tissues that connect muscle to bone. Twisting or pulling these tissues can cause a strain. Strains can happen suddenly or develop over time. Back and hamstring muscle strains are common. Many people get strains playing sports. Symptoms include pain, muscle spasms, swelling, and trouble moving the muscle.
It’s likely to be a sprain or strain if:
- pain, tenderness or weakness is experienced around the ankle, foot, wrist, thumb, knee, leg or back
- the injured area is swollen or bruised
- the patient cannot put weight on the injury or use it normally
- the patient experiences muscle spasms or cramping
Is it a sprain or a strain?
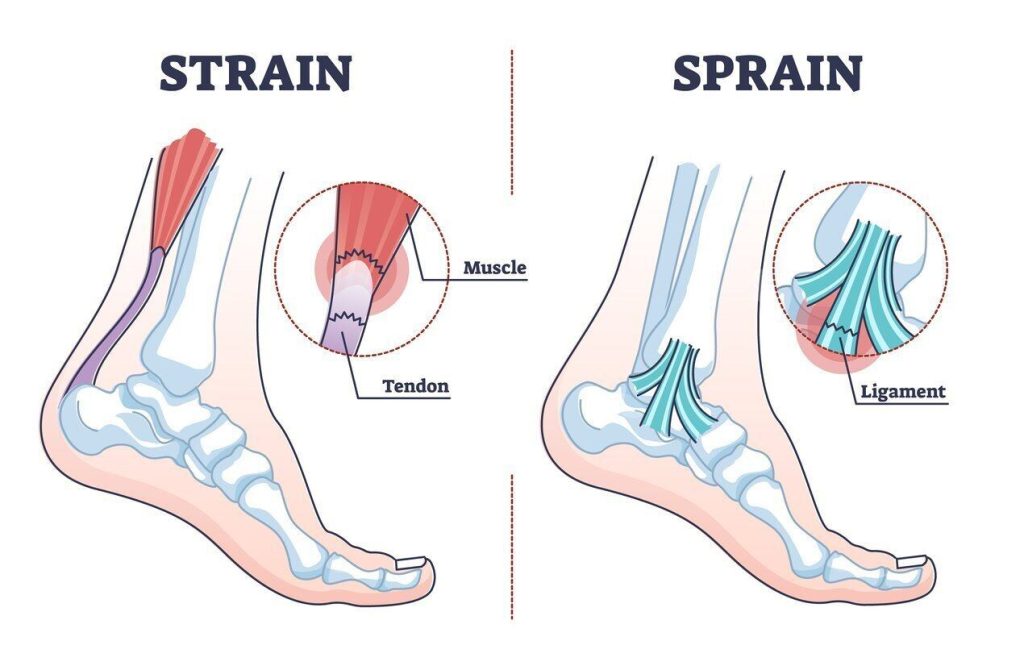
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect two bones as they sit in a joint. For example, the tibia and fibula come together to fit in the ankle joint. Tendons join those two bones together to keep the ankle stable. A joint sprain occurs when these ligaments are torn or overstretched. The ankle is the most commonly sprained joint.
Tendons are cords of tissue made up of a dense network of fibers. They connect the muscle to the bone. A joint strain occurs then the tendons or muscles tear or overstretch. The lower back and hamstrings are the most common areas for muscle strain.
Both injuries are very similar so it stands to reason that the symptoms of the injuries are also almost identical. This is why they are so commonly confused.
Symptoms of Sprains vs Strains
The symptoms for each condition is very similar, but there are some differences. The primary differences though are that bruising may occur with a sprain while a strain may elicit muscle spasms in the muscle that is affected.
Symptoms of sprains include:
- Pain around the area that is affected
- Bruising in the affected area
- Swelling in the immediate area but can expand to encompass more area
- Limited range of motion
- Decreased flexibility
Symptoms of strains include:
- Pain at the site of the joint that is affected
- Muscle spasm
- Swelling in the immediate area but can expand to encompass more area
- Limited range of motion
- Decreased flexibility
How to treat sprains and strains
For the first couple of days, follow the 4 steps known as RICE therapy to help bring down swelling and support the injury:
- Rest – stop any exercise or activities and try not to put any weight on the injury.
- Ice – apply an ice pack (or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a tea towel) to the injury for up to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours.
- Compression – wrap a bandage around the injury to support it.
- Elevate – keep it raised on a pillow as much as possible.
To help prevent swelling, try to avoid heat (such as hot baths and heat packs), alcohol and massages for the first couple of days.
