Classification of Bones
Published (updated: ).
The adult human skeleton usually consists of 206 named bones. These bones can be grouped in two divisions: axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The 80 bones of the axial skeleton form the vertical axis of the body. They include the bones of the head, vertebral column, ribs and breastbone or sternum. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes the free appendages and their attachments to the axial skeleton. The free appendages are the upper and lower extremities, or limbs, and their attachments which are called girdles.
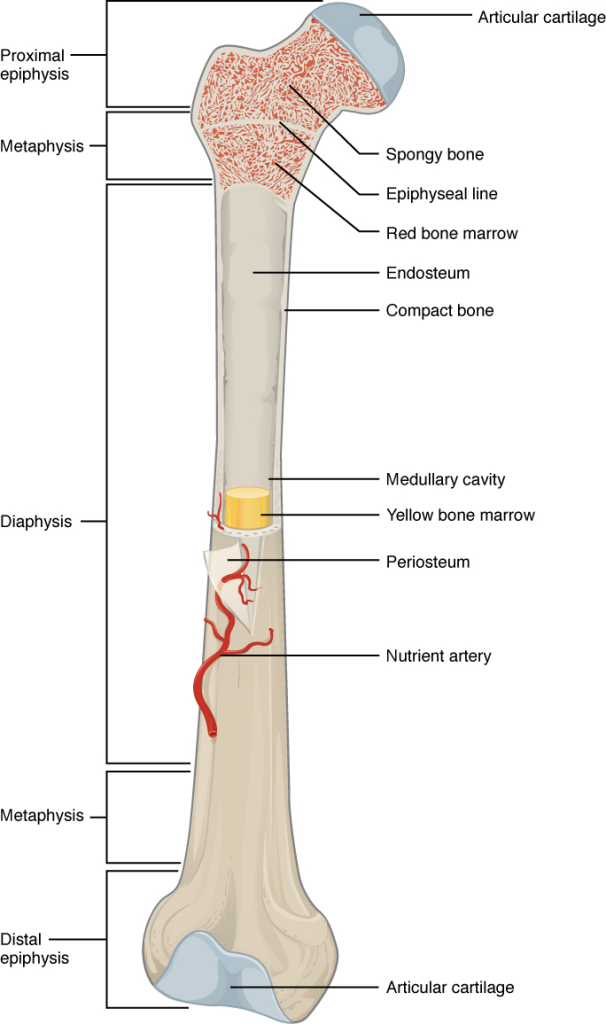
A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow. The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone.
The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Each epiphysis meets the diaphysis at the metaphysis, the narrow area that contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate), a layer of hyaline (transparent) cartilage in a growing bone. When the bone stops growing in early adulthood (approximately 18–21 years), the cartilage is replaced by osseous tissue and the epiphyseal plate becomes an epiphyseal line.
The medullary cavity has a delicate membranous lining called the endosteum, where bone growth, repair, and remodeling occur. The outer surface of the bone is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum. The periosteum contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels that nourish compact bone. Tendons and ligaments also attach to bones at the periosteum. The periosteum covers the entire outer surface except where the epiphyses meet other bones to form joints. In this region, the epiphyses are covered with articular cartilage, a thin layer of cartilage that reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber
Long Bones
The bones of the body come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The four principal types of bones are long, short, flat and irregular. Bones that are longer than they are wide are called long bones. They consist of a long shaft with two bulky ends or extremities. They are primarily compact bone but may have a large amount of spongy bone at the ends or extremities. Long bones include bones of the thigh, leg, arm, and forearm.
Short Bones
Short bones are roughly cube shaped with vertical and horizontal dimensions approximately equal. They consist primarily of spongy bone, which is covered by a thin layer of compact bone. Short bones include the bones of the wrist and ankle.
Flat Bones
Flat bones are thin, flattened, and usually curved. Most of the bones of the cranium are flat bones.
Irregular Bones
Bones that are not in any of the above three categories are classified as irregular bones. They are primarily spongy bone that is covered with a thin layer of compact bone. The vertebrae and some of the bones in the skull are irregular bones.
All bones have surface markings and characteristics that make a specific bone unique. There are holes, depressions, smooth facets, lines, projections and other markings. These usually represent passageways for vessels and nerves, points of articulation with other bones or points of attachment for tendons and ligaments.
