Vaginal Bleeding
Published .
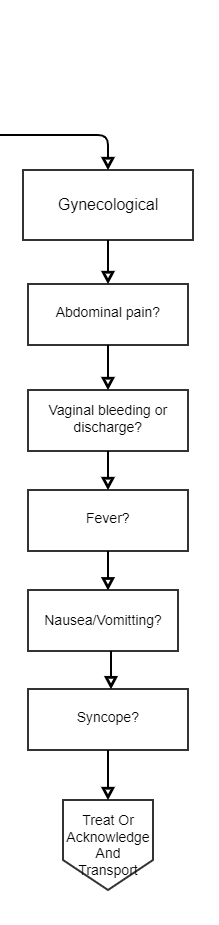
Not to overstate the obvious, a gynecological complaint should be conducted as discrete and respectful as possible. Notwithstanding, the medics need to investigate the patient’s complaint. Assess the following:
- Assess for abdominal pain – Like all abdominal pain, the most logical question is to ask is the location of the pain. Given that the abdominal organs are in various locations in the abdominal cavity, locating the pain provides valuable clues as to the origin of the patient’s pain.
- Vaginal Bleeding – If the patient is actively bleeding, inquire to the number of pads she has soaked. Obvious or significant breathing can be controlled with direct pressure to the vagina (applied by either the patient or the ambulance crew).
- Vaginal Discharge – Inquire about vaginal discharges and their odor
- Fever – Assess the patient’s temperature and inquire about a history of fever
- Nausea & Vomiting – Inquire about nausea and vomiting
- Syncope – Syncope in the presence of a gynecological problem could either mean hypovolemia from significant blood loss or sepsis.
Cases of Bleeding
Menstruation, or period, is a woman’s monthly bleeding. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is different from normal menstrual periods. It could be bleeding that is between periods, is very heavy, or lasts much longer than usual. It also includes bleeding that happens before puberty or after menopause. Causes can include:
- Uterine fibroids or polyps
- Hormone problems
- Hormone pills, such as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy (menopausal hormone therapy)
- Cancer of the cervix, ovaries, uterus or vagina
- Thyroid problems
Sexual assault is an act in which one intentionally sexually touches another person without that person’s consent, or coerces or physically forces a person to engage in a sexual act against their will. It is a form of sexual violence, which includes child sexual abuse, groping, rape (forced vaginal, anal, or oral penetration or a drug facilitated sexual assault), or the torture of the person in a sexual manner
When EMS is dispatched to a sexual assault, not only is there trauma, but also evidence. Sexual abuse patients often want to change clothes after the incident. Transporting the clothing in a paper bag will preserve evidence in the event the incident is investigated.
Cases of Infection
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
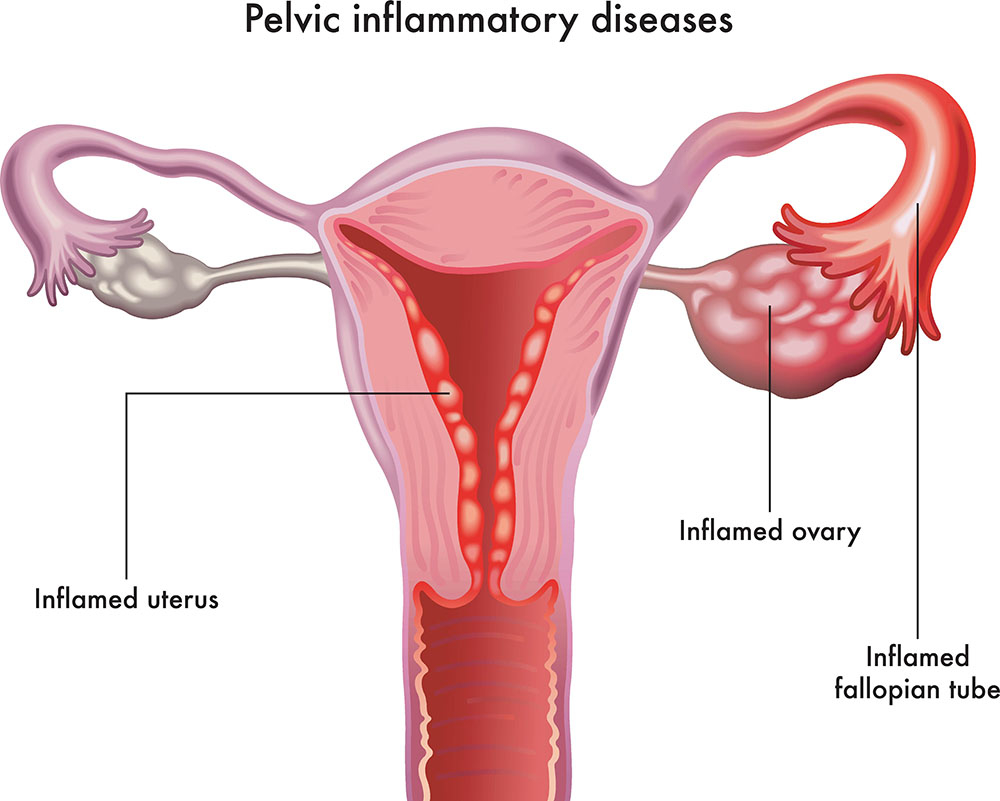
Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of a woman’s reproductive organs. It is a complication often caused by sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia and gonorrhea. Other infections that are not sexually transmitted can also cause pelvic inflammatory disease. Patients are more likely to get PID if:df
- Have an sexually transmitted diseases and do not get treated;
- Have more than one sex partner;
- Have a sex partner who has sex partners other than you;
- Have had pelvic inflammatory disease before;
- Are sexually active and are age 25 or younger;
- Douche;
- Use an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control. However, the small increased risk is mostly limited to the first three weeks after the IUD is placed inside the uterus by a doctor.
