Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment
Published .
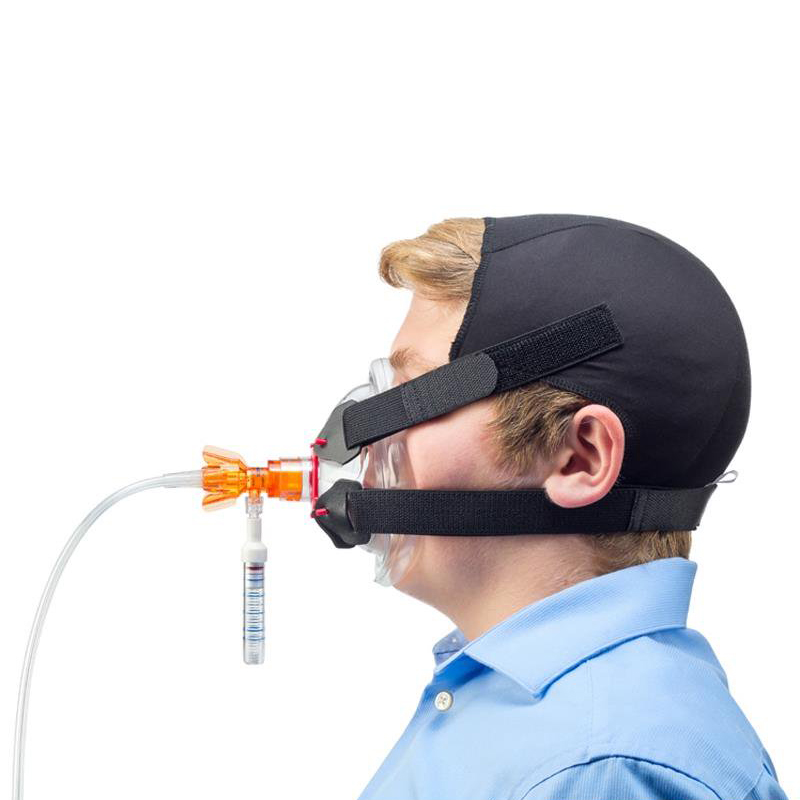
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment uses a machine to pump air under pressure into the airway of the lungs. Medics use CPAP to treat patients with pulmonary edema or congestive heart failure. The reason patients with pulmonary edema experience shortness of breath is due to high blood pressure and blood pooling in the pulmonary capillary beds. This extraneous pressure and blood prevents oxygen from diffusing into the pulmonary capillaries and leads to hypoxia. CPAP increases the air pressure in the lungs which results in better diffusion of oxygen into the pulmonary capillary beds.
More commonly, CPAP is used to treat sleep apnea. CPAP helps keep the windpipe open during sleep. The forced air delivered by CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) prevents episodes of airway collapse that block the breathing in people with obstructive sleep apnea.
Indications
- Shortness of Breath
- Congestive Heart Failure (pulmonary edema) as evidenced by crackles or clear breath sounds and hypertension
Contraindications
- Hypotension
- Uncooperative or extremely anxious patient.
- Reduced consciousness and inability to protect their airway.
- Unstable cardiorespiratory status or respiratory arrest.
- Trauma or burns involving the face.
- Facial, esophageal, or gastric surgery.
- Pneumothorax
- Copious respiratory secretions
- Severe nausea with vomiting
- Severe air trapping diseases with hypercarbia like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Most patients who have used a noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation device before need a little education about the device. It is the patient who has never used the device before or the ones that are anxious who will need help to ensure that they do not “fight” the device. The full face mask devices can cause some claustrophobe feelings for patients. Education and coaching from the medical provider are important for the patient to become comfortable and use the device. When dealing with a patient that is in an acute respiratory distress situation the prehospital provider will need to assemble the NIPPV device quickly. Ensure that the device is attached to a properly filled oxygen source because the majority of the devices will use a large amount of oxygen (refer to specific manufacturers devices) in a short period of time. Initially, just apply the mask to the face of the patient and coach them to take in deep breaths. Once the patient can tolerate the mask, then you can apply the head strap. Reassess the patient frequently for improvement in their respiratory status, lung sounds and how well they are tolerating the device.
Technique
Apply the mask to the face of the patient and coach them to take in deep breaths. Once the patient can tolerate the mask, then you can apply the head strap. Reassess the patient frequently for improvement in their respiratory status, lung sounds and how well they are tolerating the device.
