The Life Cycle of Energy Produced By Cells
Published .
Cellular Respiration is the process used by animal cells to convert nutrients to energy (ATP), and then to release waste, such as CO2. Photosynthesis is the process that plants cells use to convert light, water, and carbon dioxide to energy, and then to release waste in the form of oxygen and glucose.
All Living Things Require Energy
- Photosynthesis is the means of which plant cells get their energy.
- Cellular Respiration is the way that animals cells get their energy.
- Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration produce Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), which is a form of quick energy. When the bond holding ATP together is broken, it releases short term energy.
- Photosynthesis could not occur without cellular respiration and cellular respiration could not happen without photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast of plants while cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of animal cells.
Aerobic Respiration
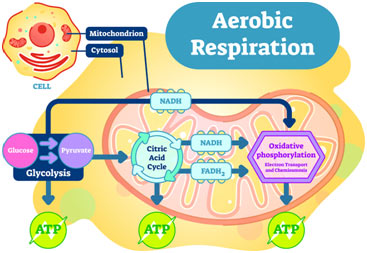
Aerobic respiration is a type of respiration that REQUIRES OXYGEN in order to function. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration in which the presence of OXYGEN IS NOT REQUIRED. An example of aerobic respiration is cellular respiration. Some examples of anaerobic respiration are alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. Photosynthesis is neither aerobic, nor anaerobic – it’s in it’s own special category. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are both used to produce ATP. However, while aerobic respiration occurs in most cells, anaerobic respiration occurs in bacteria, yeasts, and some prokaryotes. Anaerobic respiration is used when creating bread, yogurt, and beer.
Cellular respiration is the process of extracting energy in the form of ATP from the glucose in the food you eat. How does cellular respiration happen inside of the cell? Cellular respiration is a three step process. Briefly:
- In stage one, glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm of the cell in a process called glycolysis.
- In stage two, the pyruvate molecules are transported into the mitochondria. The mitochondria are the organelles known as the energy “powerhouses” of the cells. In the mitochondria, the pyruvate, which have been converted into a 2-carbon molecule, enter the Krebs cycle. Notice that mitochondria have an inner membrane with many folds, called cristae. These cristae greatly increase the membrane surface area where many of the cellular respiration reactions take place.
- In stage three, the energy in the energy carriers enters an electron transport chain. During this step, this energy is used to produce ATP.
Oxygen is needed to help the process of turning glucose into ATP. The initial step releases just two molecules of ATP for each glucose. The later steps release much more ATP.
The Reactants
What goes into the cell? Oxygen and glucose are both reactants of cellular respiration. Oxygen enters the body when an organism breathes. Glucose enters the body when an organism eats.
The Products
What does the cell produce? The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is transported from your mitochondria out of your cell, to your red blood cells, and back to your lungs to be exhaled. ATP is generated in the process. When one molecule of glucose is broken down, it can be converted to a net total of 36 or 38 molecules of ATP. This only occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
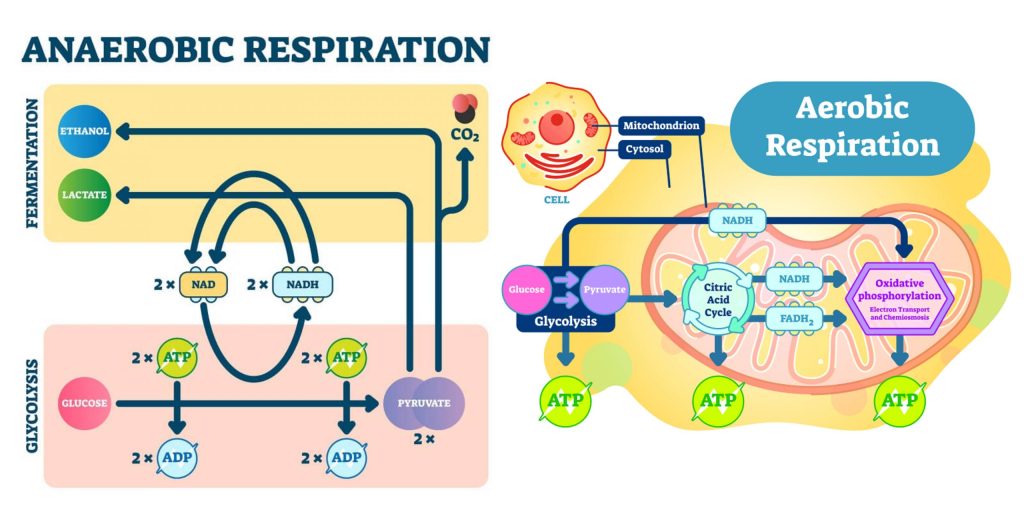
The production of energy requires oxygen. The electron transport chain, where the majority of ATP is formed, requires a large input of oxygen. However, many organisms have developed strategies to carry out metabolism without oxygen, or can switch from aerobic to anaerobic cell respiration when oxygen is scarce.
During cellular respiration, some living systems use an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor. Processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD+ from NADH are collectively referred to as fermentation. In contrast, some living systems use an inorganic molecule as a final electron acceptor. Both methods are called anaerobic cellular respiration, where organisms convert energy for their use in the absence of oxygen.
Certain prokaryotes, including some species of bacteria and archaea, use anaerobic respiration. For example, the group of archaea called methanogens reduces carbon dioxide to methane to oxidize NADH. These microorganisms are found in soil and in the digestive tracts of ruminants, such as cows and sheep. Similarly, sulfate-reducing bacteria and archaea, most of which are anaerobic, reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide to regenerate NAD+ from NADH.
Ever Felt Sore After Exercise?
The fermentation method used by animals and certain bacteria (like those in yogurt) is called lactic acid fermentation. This type of fermentation is used routinely in mammalian red blood cells and in skeletal muscle that has an insufficient oxygen supply to allow aerobic respiration to continue (that is, in muscles used to the point of fatigue). The excess amount of lactate in those muscles is what causes the burning sensation in your legs while running. This pain is a signal to rest the overworked muscles so they can recover. In these muscles, lactic acid accumulation must be removed by the blood circulation and the lactate brought to the liver for further metabolism.
