Pediatric Airway Compromise
Published (updated: ).
Initial management of pediatric patients is guided by the primary survey. The equipment used for adults such as oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways are the same for pediatric patients as they are adults, only smaller. All patients with respiratory distress should immediately be given high flow oxygen via non rebreather mask, blow by, or positive pressure ventilation. Generally, patients who are conscious will not be able to tolerate positive pressure ventilation. As a general rule, patients with signs of respiratory distress (rapid, slow, or shallow respirations), should be ventilated.
Specific to pediatric patients are conditions that lend to swelling of the airway (be it the vocal cords or epiglottis). The patient may be conscious with evidence of a airway obstruction. Comforting and oxygen administration are key to managing such a patient.
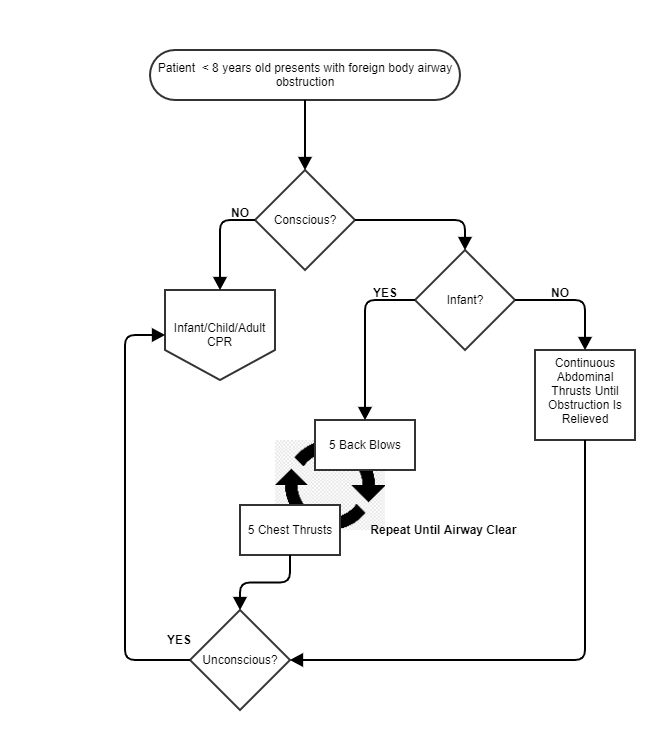
A foreign body such as a toy or secretions can create an airway obstruction. Sometimes, the obstruction can only be identified by asking the parent the SAMPLE history which would reveal a missing toy. If the patient is conscious, comforting and assisting the patient in removing the obstruction is the easiest and safest route to a clear airway. If the patient demonstrates serious work of breathing, the medics can utilize an age appropriate strategy to remove the airway obstruction.
- Conscious infants are administered alternating chest compressions and back blows in a ratio of 5 back blows then 5 chest thrusts. If the patient becomes unresponsive, switch to CPR
- Conscious toddlers and older children can be assisted with the Heimlich maneuver. If the patient becomes unresponsive, switch to CPR
Unconscious foreign body airway obstructions are treated with CPR. The CPR is performed in the same manner as a cardiac arrest, however while chest compressions are being performed, another rescuer can open the airway and attempt to visualize the obstruction. Only remove the obstruction if the object can be seen. If the obstruction can’t be seen or removed, the ventilation would be performed at the same times as would during cardiac arrest. Once chest rise with the bag valve mask has been achieved, the airway is considered clear.
