Care for the Newborn
Published (updated: ).
Most of the time, it’s not that big of a deal
Most deliveries of a newborn are uneventful. The baby is easily born with or without the help of the medical community (EMS included). The minimal care of a newborn (neonate) is to dry, warm, and stimulate. The OB kit contains blankets and wipes used to dry the baby off. No OB kit would be complete without a foil wrap and a skull cap. Usually, the baby will be active and require no further assessment. Transporting the newborn in an infant car seat is a universal standard of care. Allowing the mother to hold the newborn while she is laying on the stretcher is a recipe for disaster (imagine what would happen if the ambulance were involved in just a minor motor vehicle collision).
So what can the medics expect out of the newborn?
A healthy newborn is an active newborn that is crying. Due to the extreme pressure of being pushed through the birth canal by the mother, the lung and airway will be completely clear of any secretions. The newborn will be hungry. This is because the baby has never eaten. All of it’s calories came through the placenta. Further, there was never any need for the fetus to store any glucose, so a blood glucose level is likely to be very low. The maximum heart rate for a human is 220 minus the age. Since a newborn is age 0, the maximum heart rate is 220. It stands to reason that a neonatal heart rate will be very fast (like 150 bpm) and be completely normal. Further, since the lungs are just starting to function as they were designed, the newborn will breathe rapidly. A normal respiratory rate for a newborn is between 30 and 60 bpm.
If the newborn is not active, it’s time to go to work
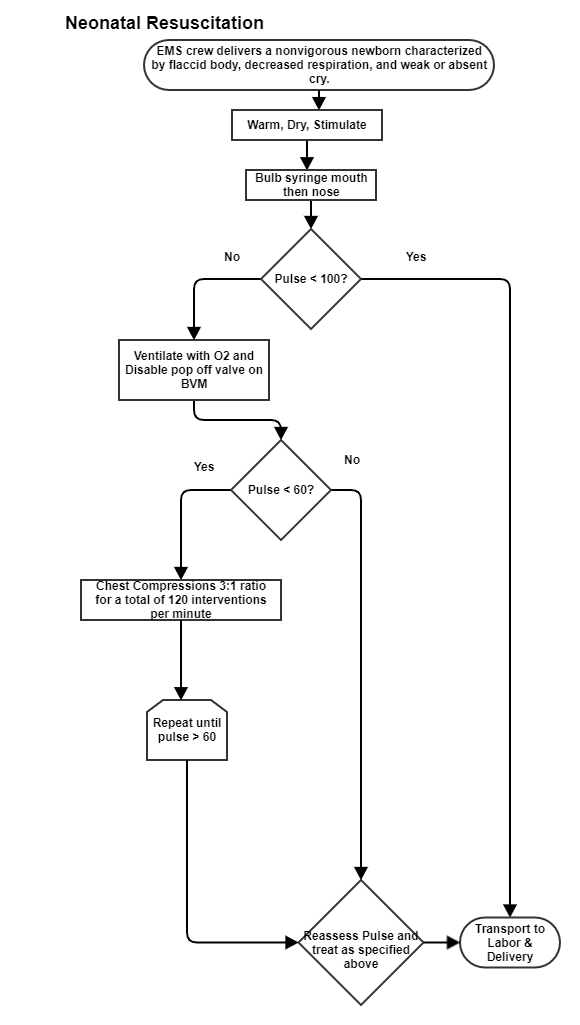
If the newborn is not active, something is wrong. Start with the airway. Use a bulb syringe to suction any secretions that could be left over from delivery. If the newborn is still not active, check the pulse on the freshly clamped and cut umbilical cord. If the pulse is under 100 but over 60, then ventilate with an infant bag valve mask with the pop off valve disabled (better yet a neonatal bag valve mask). Ventilations should be supplemented with 15 lpm of oxygen attached to the bag valve mask. If the heartrate is under 60, CPR is indicated. CPR is conveyed at a 3:1 ratio or 3 chest compressions to 1 ventilation. Chest compressions are performed using the encirclement method.
Using the APGAR to determine the health of the newborn
In every OB kit, an APGAR chart can be found. APGAR is an acronym and named after Dr. Apgar, one of the first obstetricians. The APGAR score is a universally accepted method of assessing newborns, however, not completely appropriate for EMS. Nonetheless, APGAR is as follows:
Each category is scored with 0, 1, or 2, depending on the observed condition.
Breathing effort:
- If the newborn is not breathing, the respiratory score is 0.
- If the respirations are slow or irregular, the newborn scores 1 for respiratory effort.
- If the newborn cries well, the respiratory score is 2.
Heart rate is evaluated by stethoscope. This is the most important assessment:
- If there is no heartbeat, the newborn scores 0 for heart rate.
- If heart rate is less than 100 beats per minute, the newborn scores 1 for heart rate.
- If heart rate is greater than 100 beats per minute, the newborn scores 2 for heart rate.
Muscle tone:
- If muscles are loose and floppy, the newborn scores 0 for muscle tone.
- If there is some muscle tone, the newborn scores 1.
- If there is active motion, the newborn scores 2 for muscle tone.
Grimace response or reflex irritability is a term describing response to stimulation, such as a mild pinch:
- If there is no reaction, the newborn scores 0 for reflex irritability.
- If there is grimacing, the newborn scores 1 for reflex irritability.
- If there is grimacing and a cough, sneeze, or vigorous cry, the newborn scores 2 for reflex irritability.
Skin color:
- If the skin color is pale blue, the newborn scores 0 for color.
- If the body is pink and the extremities are blue, the newborn scores 1 for color.
- If the entire body is pink, the newborn scores 2 for color.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to determine whether a newborn needs help breathing or is having heart trouble.
Normal Results
The Apgar score is based on a total score of 1 to 10. The higher the score, the better the baby is doing after birth.
A score of 7, 8, or 9 is normal and is a sign that the newborn is in good health. A score of 10 is very unusual, since almost all newborns lose 1 point for blue hands and feet, which is normal for after birth.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Any score lower than 7 is a sign that the baby needs medical attention. The lower the score, the more help the baby needs to adjust outside the mother’s womb.
Most of the time a low Apgar score is caused by:
- Difficult birth
- C-section
- Fluid in the baby’s airway
A baby with a low Apgar score may need:
- Oxygen and clearing out the airway to help with breathing
- Physical stimulation to get the heart beating at a healthy rate
Most of the time, a low score at 1 minute is near-normal by 5 minutes (4 minutes later). A lower Apgar score does not mean a child will have serious or long-term health problems. The Apgar score is not designed to predict the future health of the child.
