Bleeding
Published (updated: ).
Bleeding is the loss of blood. It can be external, or outside the body, like when you get a cut or wound. It can also be internal, or inside the body, like when you have an injury to an internal organ. Some bleeding, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, coughing up blood, or vaginal bleeding, can be a symptom of a disease.
Three types of bleeding
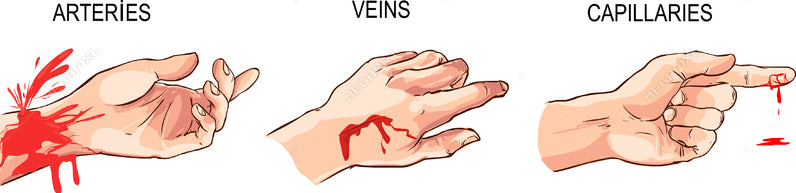
Every time your heart beats, it pumps blood through a complex network of blood vessels. These blood vessels, which control blood flow, include arteries, veins, and capillaries.
If any of these blood vessels become damaged, bleeding occurs. The type of bleeding depends on the blood vessel involved:
- Arterial bleeding. Arterial bleeding is when you bleed from an artery. Your arteries bring oxygen-rich blood away from your heart and to your body’s organs.
- Venous bleeding. In venous bleeding, blood flow comes from a vein. Your veins return deoxygenated blood to your heart.
- Capillary bleeding. Capillary bleeding is when you bleed from a capillary. Capillaries are small blood vessels that connect arteries and veins.
The most severe type of bleeding is arterial bleeding, but venous bleeding can be just as serious. You can identify venous bleeding by looking at the blood’s color and how quickly it flows out of a wound.
Venous bleeding
When a vein is torn or severed, the blood that flows out will be dark red or bluish. That’s because it no longer has oxygen. Plus, since venous blood is moving to the heart, it’s under less force than arterial blood. It will “ooze” like a thick liquid, flowing steadily out of the body. If the damaged vein is deep or large, the blood may gush out. Venous bleeding can be caused by the following wounds:
- lacerations (cuts)
- punctures
- amputations
Arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding, also called pulsatile bleeding, is the most serious type of bleeding. It’s usually caused by major injuries. Since arterial blood flows from the heart, it’s oxygenated and bright red. It will also shoot out with each heartbeat in a rhythmic pattern. This pressure can make the blood spurt up to several feet.
Compared to venous bleeding, arterial bleeding is more difficult to control. The force of each heartbeat interrupts the blood clotting process, which can lead to a lot of blood loss.
Capillary bleeding
Capillary bleeding is the most common type of bleeding. It happens whenever the skin is injured, so it occurs with all wounds. It’s less serious than other forms of bleeding.
Capillary blood oozes or trickles out of the body. It also flows quickly, but it’s usually easy to control. That’s because capillaries are small and most injuries that cause capillary bleeding are superficial.
Sometimes, if the capillaries burst due to a physical blow, the blood can get trapped beneath the skin. This produces a bruise.
